ADI Part 1 Theory Test Questions and Answers - Part 3 Driving Test
 The Official DVSA Theory Test for Approved Driving Instructors - DVD-ROM
The Official DVSA Theory Test for Approved Driving Instructors - DVD-ROM
The Official DVSA Theory Test for Approved Driving Instructors - Paperback
This publication is the official DVSA Theory Test book for Approved Driving Instructors. It will prepare you to pass the multiple choice section of your ADI theory test first time. It contains multiple choice questions from the whole theory test question bank, with answers and explanations.
ADI Theory Test 1 Questions and Answers Bank - Part 3 Driving Test
1. A 17 year-old wants to learn to drive. What must they have before they start practising on the public highway?
- A valid provisional licence
- A lesson with an approved driving instructor
- A passport
- A theory-test pass certificate
Explanation: A new driver must hold a valid provisional driving licence before they drive on the road. When they receive their licence, they should check that the details are correct.
2. A candidate taking their practical driving test is allowed to have someone accompany them on the test. How should this person behave during the test?
- They should calm the candidate
- They should take no part in the test
- They should make notes of what's said
- They should intervene if the candidate drives dangerously
Explanation: Anyone who accompanies a learner driver on a driving test must be at least 16 years old and must wear a seat belt. (This includes a person who holds a seat-belt exemption certificate.) The accompanying driver mustn't take any part in the test. The examiner can end the test if they feel any inappropriate communication has taken place.
3. A car driving-test candidate with sight in only one eye passes the test. What restriction will the examiner place on their licence?
- The licence will be restricted to vehicles with engines of less than 1500 cc
- The licence will be restricted to daytime driving only
- The licence will be restricted to adapted vehicles only
- The licence won't be restricted
Explanation: A successful candidate with vision in only one eye will be given an unrestricted pass certificate. As with all drivers, the licensing authority (DVLA) must be notified of any medical conditions when applying for a licence, and when those conditions develop or change.
4. A car is fitted with dual accelerator, clutch and brake pedals. Which of the pedals must be removed before the car can be used for a driving test?
- Clutch
- Clutch and brake
- Accelerator
- Accelerator and clutch
Explanation: Dual accelerators aren't normally fitted to training vehicles. If one is fitted, it must be removed while the vehicle is being used for a driving test.
5. A child under 3 years old is travelling in the front seat of a car. What must the driver ensure?
- The child must be carried by an adult
- The child must wear an appropriate child restraint
- The child must wear the adult seat belt where there's no appropriate child restraint
- The child must be in a rear-facing seat
Explanation: The driver must ensure that all passengers under 14 years of age wear a seat belt or sit in an approved child restraint. A child under 3 years of age, who's travelling in the front seat of a car, must use an approved child restraint.
6. A disabled driver has difficulty turning their head. What will help overcome this disability when they’re driving?
- Special seating
- Being allowed not to wear a seat belt
- Additional mirrors
- Automatic transmission
Explanation: A driver who has difficulty in turning their head will require suitably positioned additional mirrors. These will help overcome their limited zone of vision. Training and guidance will be needed in the correct and timely use of these additional mirrors.
7. A driver is convicted of drinking and driving twice within 10 years. They wish to have their licence returned. Who do they have to satisfy that they don’t have an alcohol problem?
- The Highways Agency
- The Driver and Vehicle Standards Agency
- The Disclosure and Barring Service
- The Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency
Explanation: You must be medically fit to drive. All issues relating to alcohol, drugs or health have to be reported to the DVLA Drivers Medical Group or, in Northern Ireland, the DVA Drivers Medical Section. If a licence is revoked for any health-related reason, you must reapply to the relevant medical branch and satisfy them that you're now fit to drive before they'll issue the appropriate licence for the category you require.
8. A driver (not subject to the New Drivers Act) will be disqualified if they accumulate 12 or more penalty points within what period of time?
- Three (3) years
- Four (4) years
- Five (5) years
- Six (6) months
Explanation: If a driver accumulates 12 or more penalty points within a three-year period, they must be disqualified. This will be for a minimum period of six months and may be longer if the driver has previously been disqualified.
9. A learner driver with a disability wants to take a driving test. What advice should you give them?
- Declare their disability when they apply for the test
- Go ahead with the test without telling the examiner
- Make sure they bring along their Blue Badge
- Tell their examiner which company fitted the adaptations
Explanation: A candidate should tell DVSA of any special needs or circumstances when they book their driving test. No matter how serious the disability might be, the candidate will still take the same driving test as any other person. However, more time is allowed for the examiner to discuss the candidate's needs and talk about any adaptations fitted to the vehicle.
10. A physically disabled driver passes their driving test in a specially adapted vehicle. How will their driving licence be restricted?
- They'll be restricted to vehicles fitted with suitable adaptations
- They'll have no restriction on the type of vehicle they can drive
- They'll only be allowed to drive vehicles with automatic transmission
- They'll have to keep within certain speed limits for three years
Explanation: When a physically disabled driver passes their driving test in a specially adapted vehicle, the licence issued will include restrictions. These will require the necessary modifications to be fitted to any vehicle they drive.
11. A police officer asks to see your documents. You don’t have them with you. How long do you have to produce them at a police station?
- 21 days
- 7 days
- 14 days
- 5 days
Explanation: You must be able to show your documents to a police officer when asked to do so. If you don't have them with you, you're allowed to produce them at a police station within seven days.
12. A pupil has a friend who’s agreed to help with their driving tuition. What age and driving experience must they have?
- They must be 21 or over and have held a full licence for at least two years
- They must be 21 or over and have held a full licence for at least three years
- They must be 18 or over and have a full driving licence
- They must be 18 or over and hold an advanced driver's certificate
Explanation: Anyone wishing to accompany a learner driver must be at least 21 years old and must have held (and still hold) a full licence for the category of vehicle being driven for at least three years.
13. A pupil with a physical disability is concerned that the examiner won’t understand their special needs. What should you tell them?
- They'll be tested to a lower standard than an able-bodied driver
- The examiner will have more time to study their faults
- All examiners are trained to assess the driving of candidates with special needs
- They'll have to be much better than an able-bodied driver
Explanation: All driving examiners are trained to assess candidates who have special needs. The physical disability should be declared when the test is applied for. This is to allow extra time for the
- examiner to discuss and understand how the disability affects the candidate's ability to control the vehicle
- subsequent paperwork.
14. After passing your driving test, you suffer from ill health. What must you do if your health affects your driving?
- Ask your doctor for an exemption certificate
- Inform your local police station
- Inform the licensing authority
- Get on as best you can
Explanation: You must inform the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency (DVLA), or the Driver and Vehicle Agency (DVA) in Northern Ireland, about any health condition likely to affect your driving. They'll investigate your condition and how it affects your ability to drive; they may not take away your licence.
15. An approved driving instructor (ADI) must always display red L plates (in Wales, red D or L plates or both) on the car when teaching learner drivers. What else must they display if they’re charging for the driving lesson?
- Their ADI certificate
- Their Disclosure and Barring Service (DBS) check
- Their health-and-safety certificate
- Their insurance certificate
Explanation: If an ADI is charging for a driving lesson, they must display their ADI certificate and appropriate L or D plates on the tuition car.
16. At what age does a passenger become responsible for fastening their own seat belt?
- 14 years old
- 18 years old
- 15 years old
- 16 years old
Explanation: It's the driver's legal responsibility to ensure that all passengers under 14 years old wear a seat belt, or are fastened in an approved child restraint. However, it's good practice to ensure that all other passengers wear seat belts as well.
17. At what age does category B driving entitlement normally expire?
- On your 70th birthday
- On your 65th birthday
- On your 75th birthday
- On your 60th birthday
Explanation: A category B driving entitlement is normally valid until a person's 70th birthday. The new photocard licence needs to be updated every 10 years; this is to keep the photograph up to date.
18. Drivers convicted of certain dangerous driving offences are required to take an extended driving test. How does the extended test differ from the standard driving test?
- It's the same length of time as the standard driving test but includes additional manoeuvres
- It takes about 70 minutes and includes additional manoeuvres
- It takes about 70 minutes but includes the same manoeuvres as the standard driving test
- It's focused on the cause of the candidate's conviction
Explanation: The extended test takes about 70 minutes and is assessed to the same level as the standard driving test for learner drivers.
19. For how long does a driving-test pass certificate remain valid?
- 3 years
- 1 year
- 10 years
- 2 years
Explanation: When a candidate passes a practical driving test, their full licence is normally issued directly by the licensing authority. However, if this doesn't happen, successful candidates should apply for a full licence as soon as possible. The driving-test pass certificate is valid for two years; if a full licence isn't applied for within that time, the driver will need to retake their test.
20. For how long is an MOT certificate normally valid?
- 30,000 miles
- 10,000 miles
- One (1) year
- Three (3) years
Explanation: An MOT certificate will normally be valid for one year. The certificate doesn't warrant the condition of the vehicle at a later date, but simply shows that at the time the certificate was issued the vehicle met the MOT requirements. It's the driver's responsibility to ensure that the vehicle is roadworthy whenever it's driven.
21. How many years after they’re newly registered must cars in Great Britain have an MOT test?
- One (1) year
- Seven (7) years
- Five (5) years
- Three (3) years
Explanation: A new car in Great Britain doesn't require an MOT test certificate until it's three years old. At all times, it's the driver's responsibility to ensure that the vehicle they're driving is roadworthy.
22. How often do you have to renew your photo on a photocard car driving licence?
- Every 25 years
- Every 5 years
- Every 10 years
- Every 30 years
Explanation: Photo-card licences are valid for a maximum of 10 years. This is to allow the photographic likeness to be updated when the licence is renewed. However, the licence entitlement usually lasts until age 70.
23. How should you park when you leave your vehicle overnight on a road that has a 40 mph speed limit?
- With dipped headlights on
- With parking lights on
- Facing the traffic
- Near a street light
Explanation: All vehicles must display parking lights when parked on a road with a speed limit greater than 30 mph. Park in the direction of the traffic flow so that your parked vehicle isn't mistaken for a moving vehicle.
24. How would it be illegal for a provisional licence holder to drive?
- At more than 30 mph
- If they're under 18 years old
- Without an accompanying driver
- With passengers in the rear seats
Explanation: When driving a motor car, a learner driver who holds a provisional driving licence must
- display red L plates (or D plates in Wales) to the front and rear of the vehicle
- be insured to drive the vehicle
- be accompanied by someone who's at least 21 years old and who has held for at least three years (and still holds) a full licence for the category of vehicle being driven.
25. In some circumstances, you’re allowed to park your car on the road at night without lights. It must be facing in the direction of traffic flow and at least 10 metres (32 feet) from any junction. What other restriction applies?
- The speed limit for the road must be 40 mph or less
- The road must not be a dual carriageway
- The road must not be on a bus route
- The speed limit for the road must be 30 mph or less
Explanation: To park at night without lights, you must comply with certain conditions. The road must be subject to a 30 mph speed limit, or less. Parking too close to a junction or facing the flow of traffic could confuse and cause danger for other road users.
26. The MOT certificate on your vehicle has expired. When can you drive the vehicle on the road?
- You may continue driving the vehicle providing it passes the MOT test within one calendar month
- You may drive the vehicle to and from an MOT test appointment
- You must arrange for the MOT testing station to collect the vehicle on a trailer
- You can drive the vehicle when you've told your insurance company
Explanation: Vehicles that require an MOT certificate mustn't be driven on the road after the certificate has expired. Exceptionally, the vehicle may be driven to and from a pre-arranged MOT test appointment or to a garage for repairs required for the test.
27. Tyres on cars, light vans and trailers must have a continuous tread depth of at least 1.6 mm. How much of the tyre must have this depth of tread?
- The whole width of the tyre
- The central three-quarters of the width of the tyre
- The outside half of the tyre
- At least half the width of the tyre
Explanation: Your safety and that of others may depend on the condition of your tyres. You must check that they're correctly inflated and have sufficient tread depth. The legal minimum tread depth for cars is 1.6 mm. This depth should be across the central three-quarters of the breadth of the tyre and around the entire circumference.
28. Under the New Drivers Act, a new driver will have their licence revoked if they get six or more penalty points on their licence. This only applies to drivers after they pass their first practical driving test. Over what period of time does it apply?
- 5 years
- 4 years
- 2 years
- 3 years
Explanation: Special rules apply to drivers within two years of the date of passing their first driving test. If the number of penalty points on their licence reaches six or more as a result of offences they commit before the two years are up (including any points they acquired before passing their test), their licence will be revoked. If that happens, they must start again from the beginning: apply for a provisional licence and go through the qualifying process as a learner driver, with all that this entails.
29. Until you’re 70 years old, how often should you renew your photocard driving licence?
- Every 10 years
- Every 15 years
- Every 20 years
- Every 5 years
Explanation: Photocard licences have to be renewed every 10 years until the age of 70. This is to make sure that the photograph is a good likeness of the licence holder.
30. What can a candidate do if they consider that their driving test wasn’t conducted properly?
- Write to the chief executive of the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency
- Complain to the manager of the driving-test centre
- Appeal to the Magistrates' Court in England and Wales or the Sheriff's Court in Scotland
- They have no right of appeal, other than discussing the matter with the examiner concerned
Explanation: It must be appreciated that the examiner's decision can't be changed. However, if the candidate believes that the test wasn't conducted properly, they have the right to appeal to the Magistrates' Court in England and Wales or the Sheriff's Court in Scotland.
31. What do you need before you can drive legally?
- A vehicle handbook
- Insurance cover
- Breakdown cover
- Proof of your identity
Explanation: Before you drive a vehicle on the road, you must hold a driving licence for the class of vehicle being driven. You must also be covered by a minimum of third-party insurance while driving that vehicle.
32. What does it mean if you see a pedestrian carrying a white cane that has a red band or bands wrapped around it?
- The pedestrian is blind and deaf
- The pedestrian is blind and without speech
- The pedestrian is deaf but not visually impaired
- The pedestrian is deaf and without speech

Explanation: A pedestrian who's carrying a white cane with a red band or bands is both blind and deaf. This makes them very vulnerable, since they can neither see nor hear you approaching.
33. What does it mean if your motor insurance policy has an excess of £100?
- You'll be paid £100 if you don't have a collision
- The insurance company will pay the first £100 of any claim
- You'll have to pay the first £100 of any claim
- Your vehicle is insured for a value of £100 if it's stolen
Explanation: This is a method used by insurance companies to keep annual premiums down. When you agree to an excess, it means that, in the event of a claim, you'll pay the agreed amount before the benefits of the policy will apply. Generally, the higher the excess you choose to pay, the lower the annual premium you'll be charged.
34. What lights should you use if daytime visibility is poor but not seriously reduced?
- Dipped headlights
- Rear fog lights
- Front fog lights
- Headlights and fog lights
Explanation: Only use your fog lights when visibility is seriously reduced. Use dipped headlights at other times when visibility is poor. Your headlights and tail lights help others on the road to see you. It may be necessary to turn them on during the day if visibility is reduced; for example, due to heavy rain.
35. What must a learner driver have before they drive on the road for the first time?
- A driving licence without any penalty points
- A driving-test booking
- A professional driving instructor with them
- A valid provisional driving licence
Explanation: Before taking a learner driver out for their first driving lesson, an approved driving instructor (ADI) or accompanying driver should first check the learner's
- eyesight meets the legal requirements
- driving licence is valid.
36. What must you display clearly on your vehicle while you’re being paid to give driving lessons?
- Your driving licence
- Your instructor's identification certificate
- The vehicle's MOT test certificate
- Your insurance certificate
Explanation: Approved driving instructors and trainee driving instructors are issued with an identification certificate. This must be displayed on the windscreen of a vehicle that's being used for a driving lesson.
37. What must you have when you’re renewing your vehicle tax?
- The vehicle's service record
- A valid driving licence
- The vehicle handbook
- Valid vehicle insurance
Explanation: When renewing your vehicle tax, you must have valid insurance cover for the vehicle. It's illegal to drive or keep a vehicle on public roads without insurance cover.
38. What restrictions apply to category B provisional licence holders?
- They can't drive over 50 mph
- They can't drive with passengers in rear seats
- They can't drive unaccompanied
- They can't drive at night
Explanation: Motorways mustn't be used by
pedestrians
- motorcyclists who hold provisional entitlement for the motorcycle they're riding
- riders of motorcycles under 50 cc
- cyclists
- horse riders
- agricultural vehicles
- powered wheelchairs/powered mobility scooters
- certain slow-moving vehicles and those carrying oversize loads (except by special permission).
39. What restrictions are placed on someone’s driving licence if they’re blind in one eye?
- They aren't permitted to drive a motor car
- They're only permitted to drive while they're wearing glasses
- They're required to have additional mirrors fitted to any car they drive
- Their driving licence isn't restricted in any way
Explanation: A person with only one eye isn't considered to have a disability for the purpose of driving and will be issued with an unrestricted driving licence.
40. What rule applies on a road that displays this sign?
- You mustn't stop at any time
- You may only stop to pick up passengers
- You may only stop on the verge
- The road is subject to a minimum speed limit

Explanation: Clearways are in place so that traffic can flow without the obstruction of parked vehicles. Just one parked vehicle can cause an obstruction for all other traffic. Don't stop where a clearway is in force - not even to set down or pick up passengers.
41. What rules apply to a car that’s being used for a driving test?
- It can be fitted with dual controls provided no dual accelerator is fitted
- It must be fitted with a dual brake, clutch and accelerator
- It can be fitted with dual controls, including a dual accelerator that's operable
- It must be fitted with a dual brake and dual clutch
Explanation: For safety reasons, any dual accelerator must be removed before a vehicle can be used by a candidate for their driving test.
42. What rules apply to anyone who accompanies a learner driver while they drive on the road?
- They must have held a full EC/EEA licence for the category of vehicle being driven for at least 4 years and they must be at least 21 years old
- They must have held a full EC/EEA licence for the category of vehicle being driven for at least 3 years and they must be at least 25 years old
- They must have held a full EC/EEA licence for the category of vehicle being driven for at least 3 years and they must be at least 21 years old
- They must have held a full EC/EEA licence for the category of vehicle being driven for at least 4 years and they must be at least 25 years old
Explanation: Anyone who accompanies a learner car driver must hold a full EC/EEA licence for the category of vehicle being driven, and they must have held it for at least 3 years. They must also be at least 21 years old. This applies even if they're just helping a friend and no money is exchanged.
43. What should a driver do if they’ve had a few alcoholic drinks at a party?
- Have a strong cup of coffee and then drive home
- Drive home carefully and slowly
- Wait a short while and then drive home
- Go home by public transport
Explanation: A driver who's been drinking alcohol should go home by public transport or taxi. Alcohol takes time to leave the body and someone might remain unfit to drive even the day after drinking it.
44. What should a driving-test candidate do if their inertia-reel seat belt has temporarily locked and they cannot put it on at the start of their test?
- Carry on with the test without a seat belt
- Put it on as soon as the belt has released
- Ask the examiner to postpone the test and seek a further appointment
- Ignore it and fit it sometime later
Explanation: Exemptions are provided in the regulations. If an inertia-reel seat belt has temporarily locked because the vehicle is parked on a gradient, the driver may move the vehicle. As soon as the mechanism has unlocked and released itself, the driver should stop and apply the belt.
45. What should the candidate do when the examiner gives the signal for an emergency stop?
- Depress the clutch
- Brake promptly
- Steer to the left
- Check the mirrors
Explanation: During an emergency-stop exercise, the examiner will check that the road is clear behind before they give the signal to stop. At the signal, the candidate should keep full control of the vehicle while stopping it as quickly and safely as possible.
46. What should you check before driving someone else’s vehicle?
- That the owner has left the insurance documents in the vehicle
- That the vehicle is insured for your use
- That your own vehicle has insurance cover
- That the vehicle owner has third-party insurance cover
Explanation: Driving a vehicle without insurance cover is illegal. If you cause injury to anyone or damage their property, it could be very expensive and you could also be subject to criminal prosecution.
47. What should you do if you’re taking drugs that are likely to affect your driving?
- Only drive for short distances
- Seek medical advice before driving
- Only drive if accompanied by a full licence holder
- Limit your driving to essential journeys
Explanation: Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you think that the drugs you're taking are likely to make you feel drowsy or impair your judgment.
48. What should you do when you leave your car unattended?
- Lock it and remove the key
- Leave the engine running
- Leave the hazard warning lights on
- Switch the engine off but leave the key in
Explanation: Always switch off the engine, remove the key and lock your car, even if you're only leaving it for a few minutes.
49. What should you do when you park a vehicle overnight on a road with a 40 mph speed limit?
- Park facing oncoming traffic
- Leave the dipped headlights switched on
- Leave the parking lights switched on
- Park near a street light
Explanation: When parking at night, park in the direction of the traffic flow. This will enable other road users to see the reflectors on the rear of your vehicle. You must also use parking lights where the speed limit is more than 30 mph.
50. What should you do with driving-school L plates when the vehicle isn’t being used for tuition?
- They must be covered
- They should be turned upside down
- They can remain uncovered
- They must be removed completely
Explanation: Driving instructors who always display L plates on a training vehicle are exempt from having to remove them when a full licence holder is driving the car.
51. What sort of pass certificate will the examiner issue if a disabled driver passes their driving test in a specifically adapted motor car?
- A pass certificate that limits them to driving a suitably adapted car
- A pass certificate that's unrestricted
- A pass certificate that limits them to certain speed limits for three years
- A pass certificate that states they can only drive a car with automatic transmission
Explanation: If a disabled driver passes their driving test in a specifically adapted motor car, the driving licence issued will restrict them to driving vehicles fitted with the necessary adaptations.
52. What type of car may a totally deaf person drive?
- Only a light motor car
- Any car fitted with extra rear-view mirrors
- Any type of car
- Only a car that's been suitably adapted for them
Explanation: For the purposes of driving a motor car, deafness isn't classed as a disability. Having passed their test, deaf drivers won't have their licence restricted.
53. What will a candidate be given if they fail their driving test?
- An indication of the number of lessons they need to correct their faults
- A copy of the driving-test report and an explanation of the faults
- An application for a new provisional licence
- A copy of The Highway Code and advice on how to prepare next time
Explanation: If someone fails their driving test, the examiner will give them a copy of the driving-test report form. This will show all the faults marked during the test. The examiner will also offer an oral explanation as to why they haven't passed. If the instructor is present during the examiner's explanation, they'll be able to offer their pupil additional advice and guidance.
54. What will happen if your pupil is taking their driving test but they can’t meet the eyesight requirements?
- They'll have the test cancelled
- They'll have the test postponed
- They'll be allowed to continue with the test
- They'll fail the test at once and not be asked to drive
Explanation: The eyesight test is carried out at the start of the practical driving test. If a candidate can't meet the eyesight requirements, they'll fail the test and it won't continue any further.
55. What would be invalidated if the car you’re driving doesn’t have a valid MOT certificate?
- The vehicle's excise licence
- The vehicle's service record
- The vehicle's insurance
- The vehicle's registration document
Explanation: If your vehicle requires an MOT certificate, it's illegal to drive it without one. As well as being illegal, the vehicle may be unsafe for use on the road and your insurance may be invalid.
56. What would make a car tyre illegal?
- When there's a large, deep cut in the side wall
- When it's used with a tyre of a different make on the same axle
- When it's used with a tyre of a different tread pattern on the same axle
- When it's second-hand
Explanation: Car tyres must
- be correctly inflated
- have a tread depth of at least 1.6 mm across the central three-quarters of the breadth of the tread and around the entire circumference
- be free from certain cuts and other defects.
When checking tyres for cuts and bulges in the side walls, don't forget to check the inner walls (that is, those facing each other under the vehicle).
57. What’s a cover note?
- A registration document
- A temporary insurance certificate
- An MOT certificate
- A driving licence
Explanation: Sometimes an insurance company will issue a temporary insurance certificate called a cover note. It gives you the same insurance cover as your certificate, but lasts for a limited period, usually one month.
58. What’s the first thing you should do if the vehicle you’re driving is involved in a collision?
- Call the emergency services
- Stop at the scene of the incident
- Stop, but only if people are injured
- Call your insurance company
Explanation: If you're involved in a collision that causes damage or injury to any other person, vehicle, animal or property, by law you must stop. Give your name, the vehicle owner's name and address, and the vehicle's registration number to anyone who has reasonable grounds for requiring them.
59. What’s the legal minimum depth of tread for a car tyre?
- 4.0 mm
- 1.6 mm
- 2.5 mm
- 1.0 mm
Explanation: Tyres must have enough depth of tread to give them a good grip on the road surface. The legal minimum for cars is 1.6 mm. This depth should be across the central three-quarters of the breadth of the tyre and around the entire circumference.
60. What’s the lowest level of insurance cover you must have to drive on public roads?
- Third party, fire and theft
- Third party only
- Fully comprehensive
- Personal injury cover
Explanation: The lowest level of insurance cover you must have to drive on public roads is third-party liability. The third party is anyone you might injure or whose property you might damage. With this minimum level of insurance cover, you're not covered for any damage to your vehicle or injury to yourself.
61. What’s the maximum authorised mass (MAM) of a category B vehicle?
- 7.5 tonnes
- 3.5 tonnes
- 3.0 tonnes
- 5.0 tonnes
Explanation: Any more weight than this will take the vehicle into a different category, therefore making it unsuitable for a category B driving test.
62. What’s the minimum distance from which an approved driving instructor (ADI) must be able to read a current-style (since 2001) number plate?
- 36.0 metres (120 feet)
- 20.5 metres (67 feet)
- 26.5 metres (87 feet)
- 30.5 metres (100 feet)
Explanation: Potential driving instructors (PDIs) will have their eyesight tested at the start of their Part 2 examination. A number plate, where the letters and figures are 79 mm tall and 50 mm wide, must be read at a minimum distance of 26.5 metres (87 feet). If a PDI can't pass this test, their Part 2 examination will go no further. This won't, however, affect their licence to drive, as the ADI eyesight test standard exceeds the legal eyesight requirement.
63. What’s the minimum distance from which an approved driving instructor (ADI) must be able to read a number plate that has letters and figures 79 mm high and 50 mm wide?
- 22.7 metres (75 feet)
- 30.5 metres (100 feet)
- 26.5 metres (87 feet)
- 46.0 metres (150 feet)
Explanation: There's an eyesight test for the Register of Approved Driving Instructors. The requirement is that an instructor must be able to read a number plate with letters and figures 79 mm high and 50 mm wide at a minimum distance of 26.5 metres (87 feet). This is a greater distance than the minimum legal requirement for car drivers.
64. What’s the minimum distance from which an examiner will ask a driving-test candidate to read a modern-style number plate?
- 18 metres
- 25 metres
- 22 metres
- 20 metres
Explanation: A candidate must be able to read a modern-style number plate (made after 1 September 2001) from 20 metres. If the candidate's eyesight isn't up to the required standard, the test will go no further and they'll have failed.
65. What’s the minimum driving age for a person receiving the enhanced rate of the mobility component of Personal Independence Payment?
- 15 years
- 21 years
- 16 years
- 17 years
Explanation: A 16 year old may drive a car if they're in receipt of the enhanced rate of the mobility component of Personal Independence Payment. However, if the enhanced rate is withdrawn, the normal minimum age for driving a car (17 years old) will then apply.
66. What’s the national speed limit for a car on a dual carriageway?
- 50 mph
- 60 mph
- 30 mph
- 70 mph
Explanation: Dual carriageways and motorways share the same 70 mph national speed limit for cars and motorcycles. If a car or motorcycle is towing a trailer, then this maximum permitted speed is reduced to 60 mph.
67. What’s the national speed limit on a two-way road outside a built-up area?
- 60 mph
- 50 mph
- 30 mph
- 70 mph
Explanation: The national speed limit for a car or motorcycle on a single carriageway is 60 mph. You don't have to drive at the speed limit. Use your judgement and keep within the speed limit while driving at a speed that suits the road, weather and traffic conditions.
68. What’s the nearest you may park to a junction?
- 20 metres (66 feet)
- 15 metres (49 feet)
- 12 metres (39 feet)
- 10 metres (32 feet)
Explanation: Don't park within 10 metres (32 feet) of a junction (unless in an authorised parking place). This is to allow drivers emerging from, or turning into, the junction a clear view of the road they're joining. It also allows them to see hazards such as pedestrians or cyclists at the junction.
69. What’s the speed limit on a motorway for a car towing a trailer?
- 40 mph
- 60 mph
- 70 mph
- 50 mph
Explanation: The maximum permitted speed for a car on a motorway is 70 mph, but if a car is towing a caravan or trailer, the speed limit is reduced to 60 mph. Also, vehicles towing trailers may not use the right-hand lane of a motorway that has more than two lanes.
70. What’s the speed limit on a road that has street lights but no speed-limit repeater signs?
- 30 mph
- 40 mph
- 60 mph
- 50 mph
Explanation: If you aren't sure of the speed limit, a good indication is the presence of street lights. If there's street lighting, the speed limit will usually be 30 mph unless otherwise indicated.
71. When are drivers allowed to remove their seat belt?
- Only when they're road testing the car following a repair
- When the seat belt is uncomfortable
- When they're carrying out any manoeuvre that involves reversing
- Only while they're parking their car
Explanation: Drivers are allowed to remove their seat belt when carrying out any manoeuvre that involves reversing. When the manoeuvre is complete, the seat belt must be fastened before driving away.
72. When are projection markers required on an overhanging load?
- When the load overhangs the front or rear of the vehicle by more than 2.0 metres
- When the load overhangs the front or rear of the vehicle by more than 0.5 metres
- When the load overhangs the front or rear of the vehicle by more than 1.5 metres
- When the load overhangs the front or rear of the vehicle by more than 1.0 metres
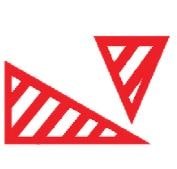
Explanation: If a load overhangs the front or rear of a vehicle by more than 2.0 metres (6 feet 6 inches), projection markers are required.
73. When can car drivers use a cycle lane identified by this sign?
- During the times shown
- Outside the times shown
- Never
- At any time
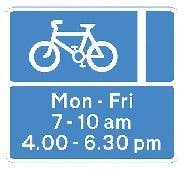
Explanation: The sign shows a mandatory cycle lane, and drivers mustn't park or drive in it during its times of operation. The lane will be marked by a solid white line on the road. Where the cycle lane is advisory, it will be marked by a broken white line. There'll also be a similar sign that shows a cycle on a blue background but without the lane represented. Don't drive in this lane unless it's unavoidable.
74. When can you use a mobile phone while you’re driving?
- When you're satisfied that no other traffic is near
- When you have a passenger who can steer for you
- When you're able to drive one-handed
- When there's a genuine emergency
Explanation: It's illegal to use a mobile phone while you're driving (except for genuine emergencies). Driving requires your total attention and concentration at all times. Using a mobile phone will distract you and increase your chances of having a collision. Even using a hands-free system will distract you. Be safe: switch off your phone before you start driving and pick up any messages when you stop for a break.
75. When can you use your front fog lights?
- At any time, so that you're noticed
- Instead of main-beam headlights
- When visibility is 100 metres (328 feet) or less
- When you're dazzled by the lights of oncoming vehicles
Explanation: Only use front fog lights when adverse weather conditions mean you can't see more than 100 metres (328 feet). Remember: to avoid dazzling other drivers, turn off your fog lights when the visibility improves.
76. When may you use your front fog lights?
- When your headlights aren't working
- When you don't want to sound your horn
- When you want extra light at night
- When visibility is seriously reduced
Explanation: Fog lights will help others see you, but they must only be used if visibility is seriously reduced. You must turn fog lights off when visibility improves, to avoid dazzling other road users.
77. When may you use your vehicle’s horn while you’re driving in a built-up area?
- Between 4.00 am and 7.00 am
- Between midnight and 6.00 am
- Between 7.00 am and 11.30 pm
- Between 11.30 pm and 6.00 am
Explanation: You mustn't sound your vehicle's horn in a built-up area while stationary on the road, or between the hours of 11.30 pm and 7.00 am. The exception is if another road user poses a danger.
78. When must you show your motor insurance certificate?
- When your vehicle is having an MOT inspection
- When you've been involved in an incident
- When you've bought or sold a vehicle
- When you're taking your driving test
Explanation: The details on your motor insurance certificate show who, when and what's insured. You'll have to produce the certificate if you've been involved in an incident and when requested by the police.
79. When will an approved driving instructor (ADI) be subject to standards checks?
- Only for the first 12 months that they're on the register
- Only until they achieve a Grade A
- For the whole time that they're on the register
- Only for the first 6 months that they're on the register
Explanation: As part of the regulations, an ADI must undergo at least one standards check during each four-year period that they're on the register. The standards check should be approached with a positive attitude and looked upon as a development opportunity.
80. Where is parking prohibited?
- In a side road
- In a one-way street
- Near a police station
- On zigzag lines near a pedestrian crossing
Explanation: Parking near a pedestrian crossing creates an obstruction that prevents both drivers and pedestrians from having a clear view. Careless parking is selfish and could endanger other road users.
81. Where would parking be likely to cause an obstruction?
- In a lay-by
- Where the kerb has been lowered for wheelchairs
- Where the kerb is raised
- In a parking bay
Explanation: Careless or thoughtless parking can create problems for other people. For example, if the kerb has been lowered to enable wheelchair access, then keep it clear. Don't park on the pavement, as this may create danger for pedestrians, who will have to move into the road to pass your vehicle. Think about the effect your parking will have on others.
82. Which lights should you use when you’re driving in daylight and it’s foggy?
- Sidelights
- Full-beam headlights
- Dipped headlights
- Hazard warning lights
Explanation: If you have to drive in fog during daylight, use dipped headlights. If visibility is below 100 metres (328 feet), use high-intensity fog lights; they help other road users to see you.
83. Which vehicle should display a flashing amber light when it’s being used on a dual carriageway?
- A mobility scooter
- An off-duty fire engine
- A non-emergency ambulance
- An emergency doctor's vehicle
Explanation: An amber flashing light on a vehicle indicates that it's slow-moving. Mobility scooters used by disabled people are limited to no more than 8 mph. On dual carriageways, they must display an amber flashing light.
84. Which vehicles aren’t allowed in the right-hand lane of a three-lane motorway?
- Vehicles towing a trailer or caravan
- Motorcycles
- Vans
- Motorcycles fitted with a sidecar
Explanation: A 60 mph speed limit applies to a vehicle towing a trailer on a motorway; such a vehicle is also not allowed in the right-hand lane of a motorway that has more than two lanes.
85. Which vehicles aren’t allowed to use the right-hand lane of a three-lane motorway?
- People carriers with seven seats
- Vehicles towing a trailer
- Vehicles under 3.5 tonnes
- Motorcycles
Explanation: Vehicles towing trailers are subject to a speed limit of 60 mph on motorways and dual carriageways. In addition, any vehicle towing a trailer may not use the right-hand lane of a motorway that has three or more lanes.
86. Which vehicles aren’t permitted to use motorways?
- Vehicles towing trailers
- Agricultural vehicles
- Motorcycles over 125 cc
- Double-deck buses
Explanation: Some vehicles are prohibited from using the motorway. These include motorcycles under 50 cc, cyclists, horse riders, agricultural vehicles and powered wheelchairs/mobility scooters.
87. Who can accompany a candidate on their driving test?
- Only a family member
- No other person
- Anyone aged 16 or over
- Only their driving instructor
Explanation: At the start of the practical driving test, the examiner will ask the candidate if they wish their instructor or accompanying driver to be present during the test. Anyone who does accompany the candidate must be 16 years or older and must wear a seat belt during the test.
88. Who can supervise a learner car driver?
- Someone who is 21 (or over) and has held a full licence for that category of vehicle for at least one year
- Someone who is 18 (or over) and who has held a full licence for that category of vehicle for at least one year
- Someone who is 20 (or over) and has held a full licence for that category of vehicle for at least three years
- Someone who is 21 (or over) and has held a full licence for that category of vehicle for at least three years
Explanation: A person who accompanies a learner driver must be at least 21 years old and must have held a full EC/EEA driving licence for the category of vehicle being used for at least three years. All approved driving instructors (ADIs) will meet these criteria.
89. Who can supervise a learner driver?
- Someone who's at least 21 years old and has held a full licence in that category of vehicle for the last three years
- Someone who's at least 25 years old and has held a full licence in that category of vehicle for the last year
- Someone who's at least 20 years old and has held a full licence in that category of vehicle for the last three years
- Someone who's at least 21 years old and has held a full licence in that category of vehicle for the last year
Explanation: Anyone supervising a learner driver must be at least 21 years old and must have held (and still hold) a full licence for the category of vehicle being driven for at least three years.
90. Who’s responsible for ensuring that a 16 year-old passenger wears a seat belt?
- The car driver
- The car owner
- The 16 year-old
- The parent/guardian
Explanation: Passengers over 14 years old are responsible for wearing a seat belt when travelling in a vehicle, unless they're exempt. A responsible driver will make sure that passengers have fastened their seat belts before setting off.
91. Who’s responsible for making sure that a vehicle isn’t overloaded?
- The person who loaded the vehicle
- The licensing authority
- The driver
- The owner of the items being carried
Explanation: If you wish to carry a heavy load on your vehicle, it's your responsibility to ensure that the load is secure and the vehicle isn't overloaded.
92. Why is it dangerous to leave rear fog lights on when they’re not needed?
- They could cause the battery to fail
- They could overload the electrical system
- They can be confused with brake lights
- They could stop the indicators working properly
Explanation: If you don't switch off rear fog lights when the fog has lifted, drivers behind may find it difficult to see your brake lights. This can be a particular problem on wet roads and on motorways. If you leave your rear fog lights on at night, drivers behind are likely to be dazzled and this could put you both at risk.
93. Why is it illegal to use a hand-held mobile phone while you’re driving?
- It will distract your attention from the road
- It will affect your satellite navigation system
- It will reduce your field of vision
- It will affect your vehicle's electronic systems
Explanation: Using a hand-held mobile phone while you're driving is illegal. Driving requires all of your attention, all of the time. Any distraction, however brief, is potentially dangerous and could affect your control of the vehicle. Even using a hands-free system will distract you. The only safe way is to switch your phone off and make or pick up calls when you stop for a rest break.
94. You find that your eyesight has become very poor. Who must you inform if your optician says they can’t help you?
- An approved optician
- The licensing authority
- The police
- Your doctor
Explanation: One condition of holding a driving licence is that you must inform the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency (DVLA), or the Driver and Vehicle Agency (DVA) in Northern Ireland, if your health deteriorates in any way that affects your ability to drive. This also applies if your eyesight deteriorates to the point that you can no longer meet the driver's eyesight requirements.
95. You have a pupil who is colour-blind. How will this affect their ability to drive?
- They're not legally allowed to drive
- They're allowed to drive without restriction
- They must have a doctor's certificate allowing them to drive
- They must have glasses with special lenses
Explanation: A person who's colour-blind will have to take exactly the same practical driving test as any other candidate. No restriction will be placed on their driving licence when they pass their test.
96. You must use your headlights when visibility is seriously reduced. What distance would be classed as seriously reduced?
- 100 metres (328 feet) or less
- 175 metres (572 feet) or less
- 125 metres (408 feet) or less
- 150 metres (490 feet) or less
Explanation: It's advisable to use headlights when visibility is poor, but they must be used when visibility is seriously reduced. This is generally when you can't see more than 100 metres (328 feet). Front and rear fog lights may also be used, but you must switch them off again when visibility improves.
97. You need glasses to bring your eyesight up to the required standard. When must you wear them?
- Only in bad light or at night time
- At all times when you're driving
- Only in bad weather conditions
- Only when you think it's necessary
Explanation: Drivers must be able to read a modern vehicle number plate from a distance of 20 metres. If you need glasses to do this, then you must wear them at all times when you're driving.
98. You want to use your mobile phone to make a personal call while you’re driving. What must you do if it has no hands-free facility?
- Hold the phone in your right hand
- Park safely before using the phone
- Slow down to less than 30 mph before using the phone
- Drive carefully while you're using the phone
Explanation: It's illegal to use a hand-held mobile phone while driving, except in a genuine emergency. Make sure you park in a safe and convenient place before receiving or making a call or text message.
99. Your car is fitted with a dual accelerator pedal. What must you do before using the car for a driving test?
- Ensure the dual accelerator pedal is in working order
- Put a rubber boot over the dual accelerator pedal
- Remove the dual accelerator pedal
- Display a sign warning that the car is fitted with a dual accelerator pedal
Explanation: It's a requirement of the driving test that if a dual accelerator pedal is fitted to a vehicle, it must be removed before the test.
100. Your car is fitted with seat belts. When can a passenger travel in your car without wearing a seat belt?
- When they're under 1.5 metres (5 feet) in height
- When they're sitting in a rear seat
- When they're under 14 years old
- When they're exempt for medical reasons
Explanation: Where fitted, seat belts must be worn. It's the driver's responsibility to ensure that children under 14 years old wear a seat belt or use a suitable child restraint. Passengers aged 14 or over are responsible for wearing their seat belt. Exceptions to this law are made for people who hold a medical exemption certificate.
101. Your pupil has just passed their first practical driving test. What will they have to do if they get six penalty points on their licence within two years?
- Retake only the theory test
- Retake only the practical test
- Reapply for a full licence immediately
- Retake the theory and practical tests
Explanation: The New Drivers Act was introduced in an attempt to reduce the high number of road traffic incidents involving new, inexperienced drivers. It states that a driver's licence will be revoked if they receive six or more penalty points as a result of offences committed within two years of passing their first practical driving test.
102. Your pupil is at the end of their driving test. With your pupil’s permission, what does DVSA advise you to do?
- Request a separate debrief
- Listen to the debrief
- Keep out of sight to avoid distraction
- Request a personal written report
Explanation: Subject to the candidate's permission, instructors are encouraged to accompany their pupils on their driving test and also to listen to the examiner's debrief. If they haven't been present during the test, instructors are advised to be available to listen to the examiner's debrief at the end of the test.
103. Your pupil, who is profoundly deaf, intends to apply for a driving test. What advice should you give them about their application?
- Complete an application form for an extended test
- Don't declare their deafness
- Declare their deafness on the application form
- Complete an application form for a special test
Explanation: The Driver and Vehicle Standards Agency will need to know that your pupil is profoundly deaf to make the appropriate booking arrangements. This should be recorded when booking the test. Approved driving instructors should be able to help any pupil with their application for a theory test or a practical driving test.
104. Your vehicle has been involved in a collision with another vehicle. Some damage has occurred. What must you do after you’ve stopped?
- Report the incident to the police some time within the next seven days
- Give your name and address to all witnesses
- Show the other driver your registration and MOT certificates
- Give your own and the vehicle owner's name and address to anyone having reasonable grounds for requiring them
Explanation: If you're involved in a collision that causes damage or injury to any other person, vehicle, animal or property, you must stop and exchange details with anyone having reasonable grounds for requiring them. If you don't give your details at the time, report the incident to the police as soon as is reasonably practicable and in any case within 24 hours.
105. Your vehicle is fitted with a hands-free phone system. What’s likely to happen if you use this equipment while you’re driving?
- You'll notice an improvement in your hazard perception
- Your driving will be unaffected
- You'll have trouble hearing the phone conversation
- Your attention will be distracted away from driving
Explanation: It's illegal to use a hand-held mobile phone while driving. Using a hands-free system doesn't mean that you can hold a conversation and drive safely at the same time; it will still distract your attention from the road. Act responsibly and wait until you've parked before using your mobile phone.
106. Your vehicle is stationary in traffic. When are you allowed to use the horn?
- At any time you wish
- To signal that you're in a hurry
- If your hazard warning lights aren't working
- When a moving vehicle may cause you danger
Explanation: If your vehicle is stationary, only sound the horn if you think there's a risk of danger. Don't use it to attract attention. This causes unnecessary noise and could be misleading to other road users.
107. You’re driving a car. What should you do before answering a call on your mobile phone?
- Check your mirrors
- Reduce your speed
- Stop in a safe and convenient place
- Check who's calling
Explanation: It's illegal to use a hand-held phone while you're driving. Even using a phone with a hands-free system is potentially dangerous, as it will distract your attention. The safest action is to switch your phone off while you're driving and listen to your messages or make any calls when you've stopped the car in a safe place.
108. You’re driving a friend’s children home from school. They’re both under 14 years old. Who’s responsible for making sure they wear a seat belt?
- You
- An adult passenger
- The children
- Your friend
Explanation: Child passengers should be encouraged to fasten their seat belts themselves from an early age, so that it becomes a matter of routine. It's the driver's responsibility to check that the seat belts of any passengers under 14 years old are fastened securely.
109. You’re driving along a road that has a cycle lane marked by a solid white line. What does it mean if the road sign shows that the cycle lane is in operation?
- The lane may be used when necessary
- You may drive in that lane at any time
- You mustn't drive in that lane
- The lane may be used for parking your car

Explanation: Drivers mustn't park or drive in a cycle lane that's marked by a solid white line during its periods of operation. At other times, when the lane isn't in operation, you should be aware that there may be cyclists in the area.
110. You’re driving at night on a road that has a 30 mph speed limit. You find somewhere to park near a junction. How close to the junction are you allowed to park?
- 20 metres (66 feet)
- 15 metres (50 feet)
- 25 metres (82 feet)
- 10 metres (32 feet)
Explanation: Don't park less than 10 metres (32 feet) from a junction (unless in an authorised parking place). At night, park in the direction of the traffic, so that your car's red reflectors show to passing drivers. You must use your parking lights when parking at night on a road, or in a lay-by on a road, where the speed limit is over 30 mph.
111. You’re driving at night. When can you park on the right-hand side of a road?
- When you park with your offside parking lights switched on
- When you park in a one-way street
- When you park less than 10 metres (32 feet) from a junction
- When you park under a lamppost
Explanation: Red rear reflectors show up when headlights shine on them. These are useful when you're parked at night but will only reflect if you park in the same direction as the traffic flow. Normally you should park on the left, but if you're in a one-way street you may also park on the right-hand side.
112. You’re driving at night. When can you park on the right-hand side of the road?
- When you're in a two-way street
- When the road has street lighting
- When you're in a built-up area and at least 10 metres (32 feet) from a junction
- When you're in a one-way street
Explanation: You may leave your vehicle parked on the right-hand side of the road in a one-way street. Your vehicle's red rear reflectors will then show to traffic approaching from the rear, regardless of which side of the road you park.
113. You’re driving in fog. When should high-intensity rear fog lights be used?
- When visibility is reduced to 150 metres (490 feet) or less
- When visibility is reduced to 175 metres (572 feet) or less
- When visibility is reduced to 125 metres (408 feet) or less
- When visibility is reduced to 100 metres (328 feet) or less
Explanation: High-intensity rear fog lights are far brighter than normal rear lights. When visibility is reduced to 100 metres (328 feet) or less, they should be used to help drivers behind to see your vehicle. When visibility improves, these high-intensity lights should be switched off to avoid dazzling drivers behind.
114. You’re driving in fog. When should you switch on your rear fog lights?
- When visibility has fallen to 200 metres (656 feet) or less
- When visibility has fallen to 100 metres (328 feet) or less
- When visibility has fallen to 10 car lengths
- When visibility has fallen to your overall stopping distance
Explanation: If visibility falls below 100 metres in fog, switching on your rear fog lights will help road users behind to see you. Don't forget to turn them off once visibility improves: they're very bright, so they might be mistaken for brake lights and they could dazzle other drivers.
115. You’re driving on a road that has double white lines along the centre of the road. The line nearest you is continuous. When may you cross this line to overtake?
- When you're passing a road maintenance vehicle that's travelling at less than 10 mph
- When you're passing traffic that's queuing at a junction with a major road
- When you can see there are no obstructions on the right-hand side of the road
- When you're passing a car that's slowing down to turn left into a minor road

Explanation: If there are double white lines along the centre of the road and the line nearest you is continuous, you mustn't cross or straddle the line, except in specific circumstances. These include to enter premises or a side road, or to pass a stationary vehicle. You may also overtake a bicycle, horse, or road maintenance vehicle, provided they're travelling at 10 mph or less. You mustn't park on such a road, but you may stop to pick up or set down passengers.
116. You’re driving on a two-way road. There are double solid white lines along the centre of the road. What should you do if there’s a stationary vehicle parked on the left?
- You must wait for the driver to move their vehicle
- You should report the obstruction to the police
- You may cross the solid line to pass the stationary vehicle if it's safe
- You may pass the stationary vehicle, but only if you don't cross the solid line
Explanation: Double white lines along the centre of the road are usually found in places where there's a poor view ahead, usually caused by bends in the road. When the line nearest to you is solid, you may cross it to pass a stationary vehicle, providing that it's safe to do so.
117. You’re driving with your front fog lights switched on. What must you do if the fog has cleared?
- Flash them to warn oncoming traffic that it's foggy
- Switch them off as long as visibility remains good
- Leave them on if other drivers have their lights on
- Drive with them on instead of your headlights
Explanation: Fog lights should only be used when visibility is seriously reduced. They must be switched off when visibility improves, to avoid dazzling other road users.
118. You’re entering an area of roadworks. What must you do if you see this sign?
- Obey the limit only during rush hour
- Treat the speed limit as advisory
- Obey the limit except for overnight
- Not exceed the speed limit

Explanation: Where there are extra hazards such as roadworks, it's often necessary to slow traffic down by imposing a temporary speed limit. The speed-limit sign will be circular and edged with a red ring. This tells you that the sign is an order and you must obey it
119. You’re invited to a pub lunch. What’s your best course of action if you know that you’ll have to drive in the evening?
- Have some milk before drinking alcohol
- Eat a hot meal with your alcoholic drinks
- Don't drink any alcohol at all
- Avoid mixing your alcoholic drinks
Explanation: Alcohol remains in the body for several hours; this may make you unfit to drive a long time after having an alcoholic drink. If you know you'll be driving, the safest course is to avoid drinking any alcohol.
120. You’re involved in a traffic incident. Which document will you need to produce for a police officer?
- Vehicle registration certificate
- Theory test certificate
- Driving licence
- Vehicle excise licence
Explanation: You must stop if you've been involved in a collision that results in any injury or damage. You must also be able to produce your driving licence when a police officer asks to see it. If you can't do this at the time, you may be asked to take it to a police station within a certain period. You may also be asked to show a valid insurance certificate and a valid MOT certificate.
121. You’re leaving your vehicle parked on a road. When may you leave the engine running?
- When you're in a 20 mph zone
- If the battery is flat
- If you'll be parked for less than five minutes
- Not on any occasion
Explanation: When parking, all ancillary controls should be switched off and the engine stopped. Make sure that the handbrake is applied firmly before leaving the vehicle.
122. You’re leaving your vehicle unattended. How can you reduce the chance of it being broken into?
- Cover any valuables with a jacket
- Leave any valuables in a plain carrier bag
- Lock any valuables out of sight
- Place any valuables on the parcel shelf
Explanation: When leaving your car, take all valuables with you, if you can. Otherwise, lock them out of sight.
123. You’re parking on a road that has a 30 mph speed limit. How close are you allowed to park to a junction?
- 5 metres (16 feet)
- 15 metres (49 feet)
- 25 metres (82 feet)
- 10 metres (32 feet)
Explanation: The minimum distance you should leave your car from a junction is 10 metres (32 feet) - unless you're in an authorised parking space. Parking closer to a junction makes access to it more hazardous because the parked vehicle will block a driver's view. Pedestrians trying to cross the road may also be hidden by such a parked vehicle.
124. You’re parking on the road at night. When should you use parking lights?
- When there are white lines in the middle of the road
- When you're facing oncoming traffic
- When the speed limit exceeds 30 mph
- When you're near a bus stop
Explanation: Cars, light goods vehicles, invalid carriages and motorcycles can be parked at night without lights on roads with a speed limit of 30 mph or less. They must comply with any parking restrictions and face the direction of the traffic flow.
125. You’re teaching a pupil how to turn the vehicle around. Can you remove your seat belt while you’re teaching this exercise?
- Yes, but only if the pupil holds an exemption certificate
- Yes, but only when asked to do so by the pupil
- Yes, you may remove your seat belt but only when the vehicle is actually reversing
- Yes, you may remove your seat belt during any manoeuvre that involves reversing
Explanation: Drivers and passengers must normally wear seat belts. However, a driver may remove their seat belt when carrying out an exercise that involves reversing; this also applies to driving instructors while supervising such manoeuvres.
126. You’re teaching a pupil how to turn the vehicle around. Can you remove your seat belt while you’re teaching this exercise?
- Yes, but only if the pupil holds an exemption certificate
- Yes, but only when asked to do so by the pupil
- Yes, you may remove your seat belt but only when the vehicle is actually reversing
- Yes, you may remove your seat belt during any manoeuvre that involves reversing
Explanation: Drivers and passengers must normally wear seat belts. However, a driver may remove their seat belt when carrying out an exercise that involves reversing; this also applies to driving instructors while supervising such manoeuvres.
127. You’re teaching a pupil to reverse into a side road. What’s the law governing your use of the seat belt?
- You may leave your seat belt off for the whole of the manoeuvre
- You must wear your seat belt at any time the pupil is moving forward during the manoeuvre
- You must wear your seat belt for the whole manoeuvre
- You should remove your seat belt to assist the pupil
Explanation: An instructor must normally wear a seat belt during all practical training when there's one fitted to the vehicle, unless they're exempt. However, when a pupil is carrying out a manoeuvre that involves reversing, instructors may release the belt during the exercise; this gives them a little more freedom to teach the exercise safely.
128. You’re teaching your pupil how to reverse a car into a side road on the left. What should you teach them to do if the rear nearside tyre gently touches the kerb?
- Accept that they're not ready for this exercise and drive off
- Keep going backwards until they mount the kerb and then pull forward
- Drive forward to straighten the car and then continue reversing
- Drive around the corner to where they started from and start again
Explanation: If your pupil makes a minor error when carrying out a reversing exercise, even during their driving test, it's acceptable to correct the problem before it develops into a serious fault. The correction must be carried out safely.
129. You’ve just driven out of fog. What must you do now that visibility has improved?
- Leave your fog lights on in case the fog returns
- Switch off your fog lights
- Keep your rear fog lights on
- Keep your front fog lights on
Explanation: Bright fog lights can dazzle other drivers, so you must remember to turn them off when the fog lifts and visibility improves. Be prepared for patchy fog: you may need to turn the fog lights on again.
130. You’ve parked your vehicle on the road at night. When must you leave the parking lights switched on?
- When you're facing oncoming traffic
- When the speed limit exceeds 30 mph
- When there are continuous white lines in the middle of the road
- When you're near a bus stop
Explanation: When parking on a road at night, all vehicles must display parking lights when the road has a speed limit greater than 30 mph.
www.passwithalison.co.uk is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon.com. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. www.passwithalison.co.uk participates in various other affiliate programs and we sometimes get commission through purchases made through our links.





